 January 06, 2026
January 06, 2026Calculate Driving Distance and Time at Scale with Geocodio’s New Distance API
Use Geocodio's new distance API endpoints to calculate driving and straightline distance between addresses.
Quick summary: Geocodio just launched a suite of distance calculation API endpoints that calculate driving time/distances and straightline (haversine) distance between addresses. These APIs can help you whether you need results in real time or need to process large batches in the background.
Note: Distance calculations are currently only available via API, but we plan to release support for spreadsheets in the near future. If you're interested in distance calculations via spreadsheet upload, please reach out—we're actively looking for people to give feedback on potential workflows.
How to get started with Geocodio’s Distance API
Below, you’ll find an in-depth exploration of Geocodio’s new Distance APIs. But if you’re eager to get started, here’s a quick overview:
- Distance endpoint: for synchronous single calculations (one-to-one, one-to-many)
- Distance Matrix endpoint: for synchronous batch processing, up to 10,000 calculations per batch (one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many)
- Distance Jobs endpoint for async high-volume distance calculations—up to 50,000 calculations (one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many)
Distance is a separate product from geocoding, and the distance API endpoints use credits. All customers, including Unlimited customers, need to purchase credits in order to use the distance APIs. (See more below.)
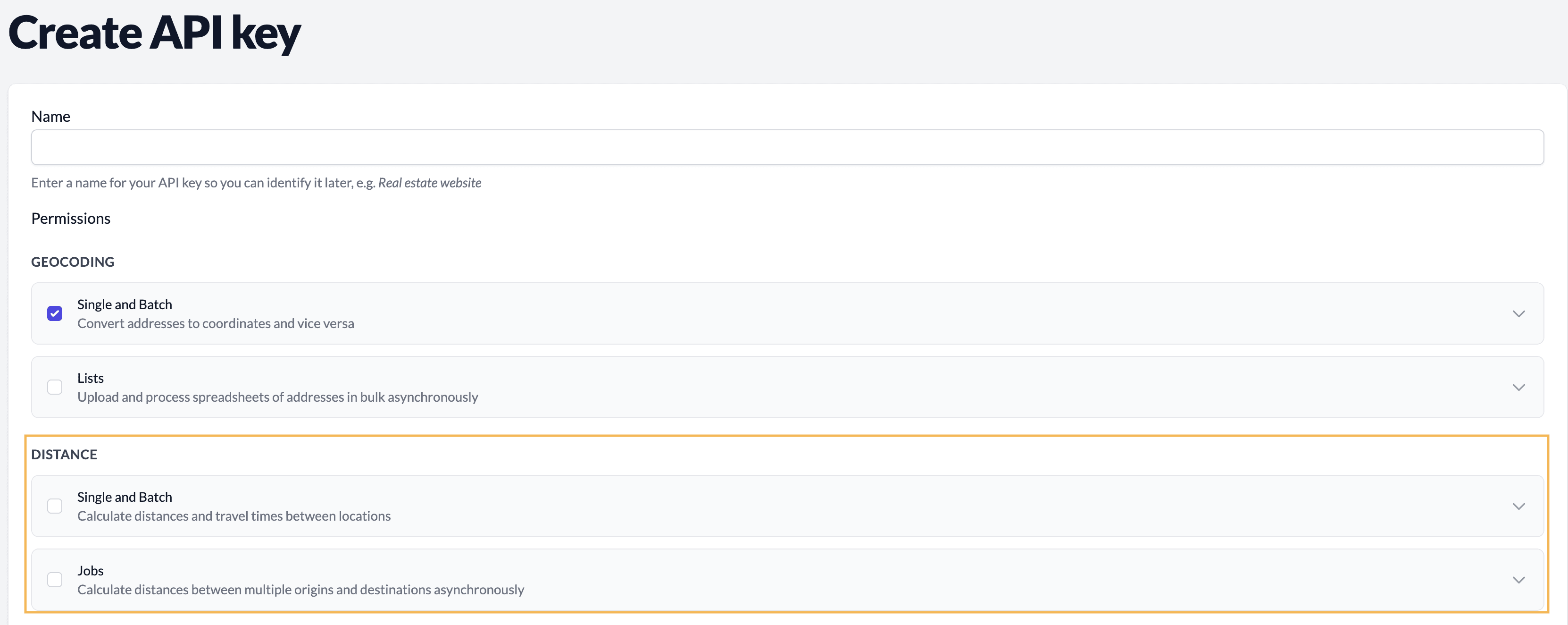
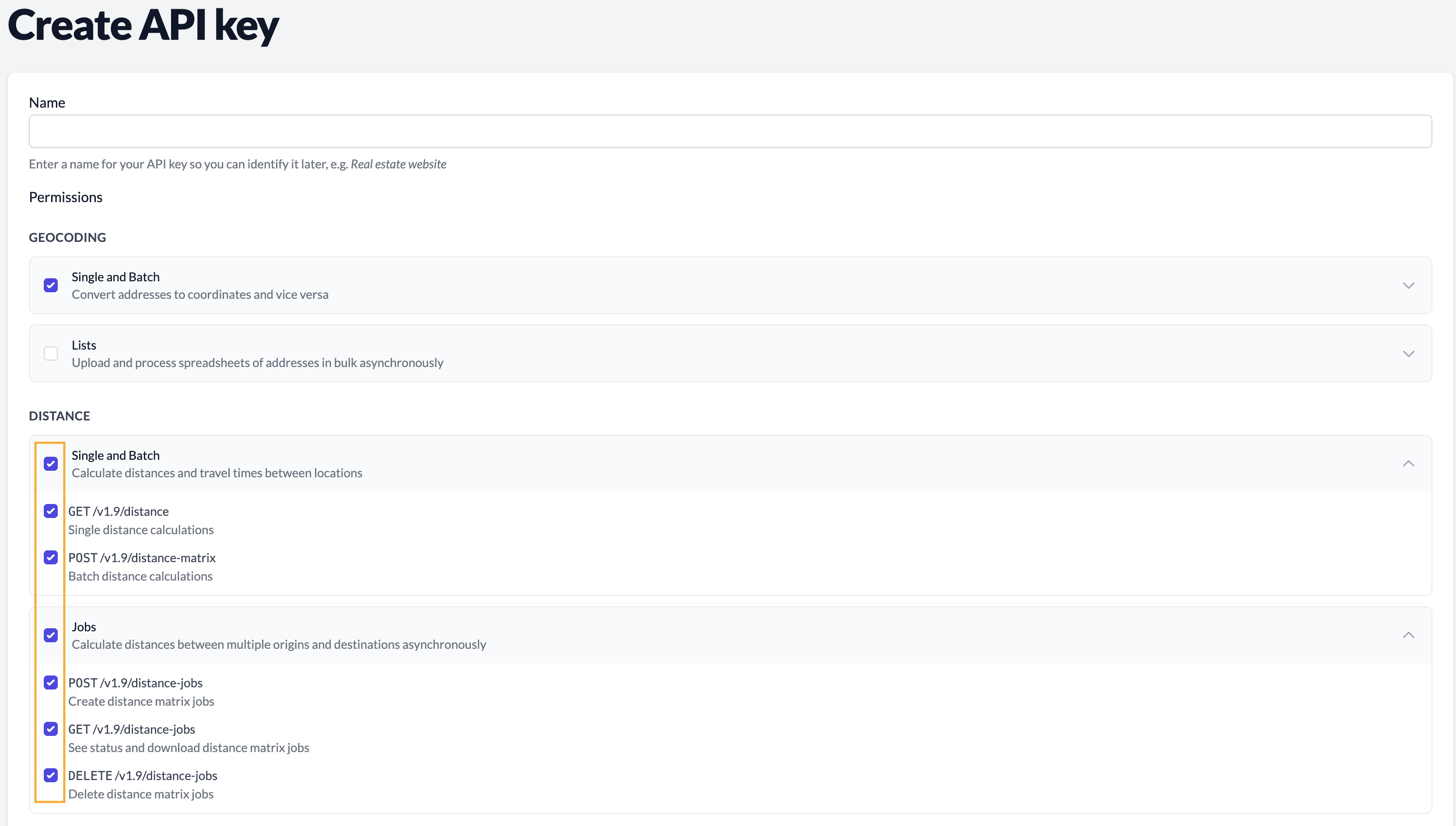
To enable Distance API access, go to the API keys page on the Geocodio dashboard and enable Distance and Distance Jobs permissions for your API key(s). (Self-Service dashboard, Enterprise dashboard—requires log-in or account creation first)
For detailed documentation and code examples, visit the Distance API documentation (Self-Service API docs, Enterprise API documentation).
Cost of using Geocodio’s Distance API
Geocodio’s Distance API uses a credit-based system based on the volume and type of calculations.
There are two components to your usage: the base geocoding cost (as coordinates are required for the calculations), and the distance calculation cost. Geocoding counts as 1 credit per address, and the distance cost is based on the type of distance (1 credit for straightline, 2 for driving) times the number of calculations.
For example, let’s say you have 1,000 patients and 50 clinic locations, and want to know the closest clinic to each patient. For straightline distance, it would be 51,050 credits, and for driving distance, it would be 101,050.
Here’s how the cost breaks down:
The base geocoding cost is based on the total number of locations added together.
→ Following our example, this portion would use 1,050 credits (1,000 patient addresses + 50 clinic location addresses).
Note: If you supply coordinates as the input, you won’t be charged for geocoding.
The distance cost is based on the type of distance and the number of calculations.
By default, Geocodio’s distance APIs will use straightline distance, which uses 1 credit per calculation. Driving distance uses 2 credits per calculation.
→ Following our example, if you were to calculate the straightline distance between your 1,000 patients and 50 clinic locations, this portion would use 50,000 credits (1,000 patient addresses x 50 clinic location addresses x 1). With geocoding, your total credits consumed would be 51,050 (1,050 credits for geocoding + 50,000 credits for straightline distance calculations).
→ If you wanted the driving time between your 1,000 patients and 50 clinic locations, this portion would use 100,000 credits (1,000 patient addresses x 50 clinic location addresses x 2). With geocoding, your total credits consumed would be 101,050 (1,050 credits for geocoding + 100,000 credits for driving distance calculations).
For Pay-As-You-Go Customers
Your daily free tier of 2,500 credits can be used towards the distance APIs.
To go beyond the free tier, you must have a valid payment method on file or purchase credits.
For Unlimited Customers
In order to make distance calculations, you will need to purchase credits, as distance is a separate product from geocoding.
However, if you have a Standard or Enterprise Unlimited subscription, the geocoding step of your distance requests will be routed through your dedicated instance. This means that the geocoding portion is essentially free, and you only have to pay for the distance calculations.
Using the above examples, your costs would then be:
→ Straightline distance between 1,000 patients and 50 clinics: 50,000 credits
→ Driving distance between 1,000 patients and 50 clinics: 100,000 credits
All Unlimited accounts have received 5,000 free credits in order to try the new Distance APIs for free. These credits have already been applied to your account and apply at the organization level (i.e. are shared across all users on your team).
Purchasing Credits
Credits do not expire, and credit packages of over 500,000 are eligible for volume discounts. See credit pricing on your dashboard (Standard | Enterprise).
Calculate Driving and Straightline Distance
Geocodio’s Distance APIs support two distance calculation modes: straightline distance and driving time/driving distance.
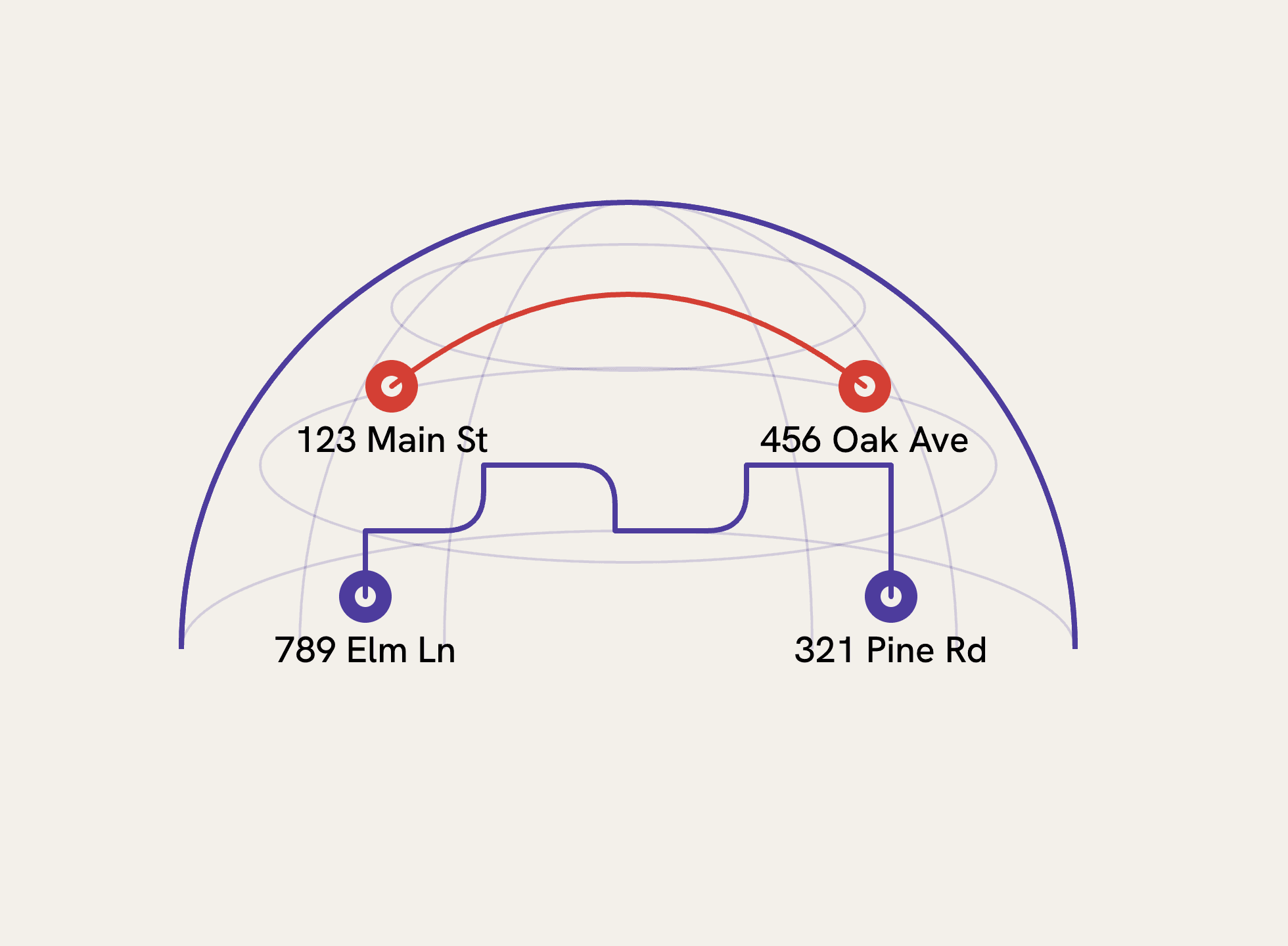
Straightline distance uses the Haversine formula to calculate the great-circle distance between two points (sometimes called "as the crow flies"). This mode is fast and useful when you need general geographic proximity, such as understanding how far gym members live from a fitness club.
Driving distance calculates actual road network distances and returns both driving distance (miles and kilometers) and typical driving time. You might use this role to give customers a rough ETA when a technician might arrive, see how far patients live from a medical facility, and other applications where people generally travel by car.
Note: Geocodio’s Distance API provides typical driving time based on average traffic patterns, not real-time traffic conditions.
Geocodio’s Distance APIs also include several filtering and sorting parameters that work across all distance endpoints:
max_distance: Limit results to locations within a certain radius (in miles or kilometers)max_duration: Filter by drive time in seconds (e.g., 1800 for 30 minutes)min_distanceandmin_duration: Exclude locations that are too closeorder_by: Sort results by distance or durationsort_order: Ascending or descending ordermax_results: Cap the number of destinations returned
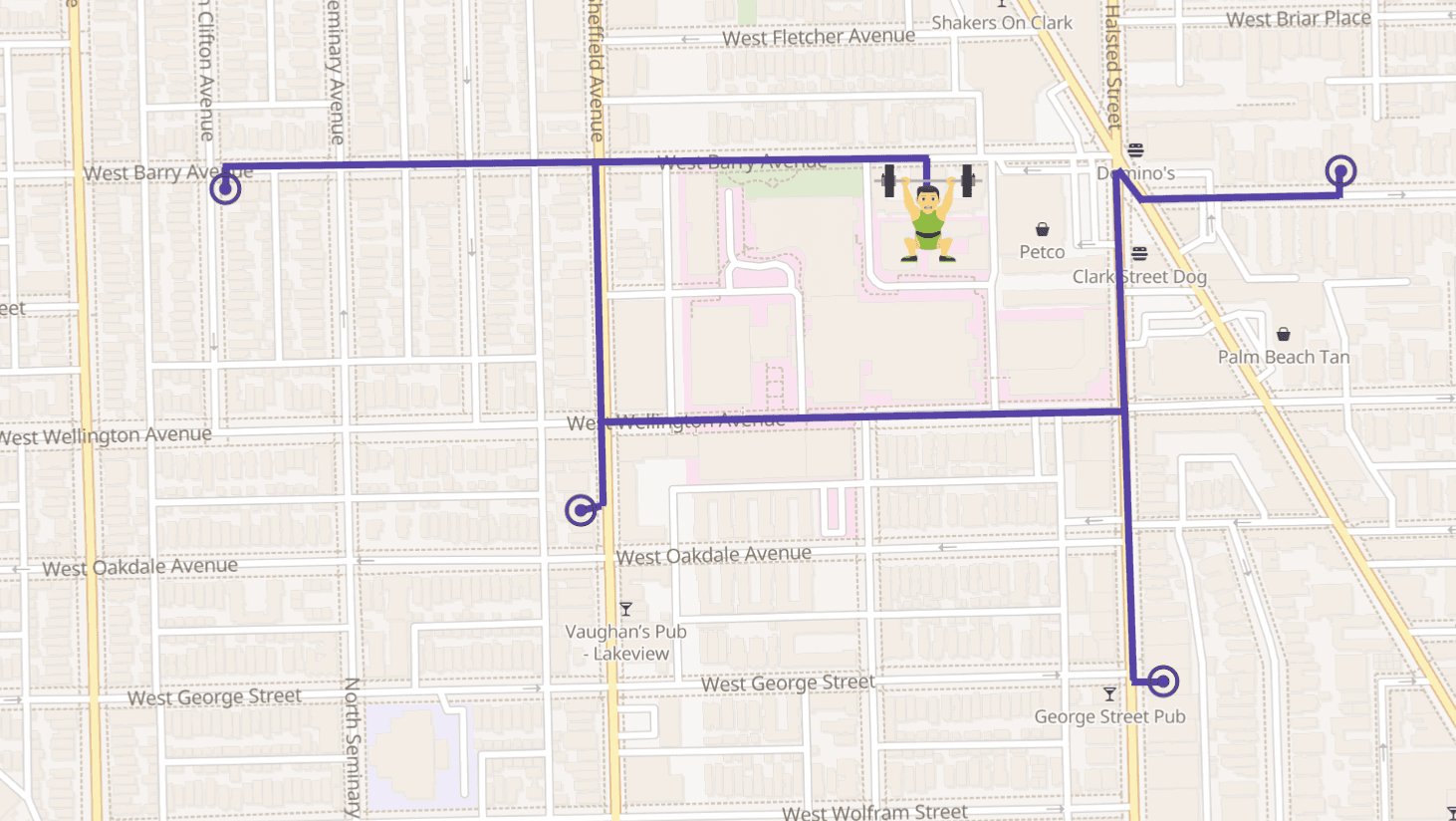
Options for Single, Batch, and High-Volume Distance Calculations
Geocodio’s distance API has three different endpoints:
- Single: Use when you need to return one-to-one distance between two addresses in real time to a user (synchronous)
2. Matrix: Use when you have multiple distance calculations or need one-to-many or many-to-many calculations and need results in real time (synchronous)
3. Jobs: Use when you have a large list of addresses or coordinates you need to calculate distance between and can let it process in background (asynchronous)
Distance Endpoint: Real-Time Single-Origin Calculations
Geocodio’s single distance endpoint calculates distances from one starting point to another, or multiple, destination(s) in real time.
This endpoint is useful when you need to provide instant distance estimates to a user. For example, if you wanted to be able to give a customer a heads up that a technician is on the way, you could use it to return the average driving time between the technician and the customer’s address.
GET https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance
?origin=technician_current_location
&destinations[]=customer_address
&mode=driving
Distance Matrix: Many-to-Many Batch Processing
Geocodio’s Distance Matrix API endpoint processes everything synchronously and returns results (grouped by origin) immediately, making it suitable for batch processing when you need a quick turnaround.
Geocodio’s Distance Matrix API can handle multiple origins to multiple destinations simultaneously—up to 10,000 calculations per request.
For example, perhaps you’re an e-commerce company’s logistics team, and you need to figure out which warehouse can deliver orders to customers fastest as orders come in. Geocodio’s Distance Matrix API would let you evaluate multiple warehouses against multiple customer addresses in a single request.
This is a POST request. The body takes a JSON object with an origins array and a destinations array.
POST https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance-matrix
{
"origins": [
"38.8977,-77.0365,warehouse_dc",
"37.3317,-122.0307,warehouse_sf"
],
"destinations": [
"41.8781,-87.6298,customer_1",
"350 5th Ave, New York, NY"
],
"mode": "driving"
}
Distance Jobs: Asynchronous Large-Scale Processing
The key difference of Geocodio’s Distance APIs compared to other options is the Distance Jobs endpoint, which lets you calculate distance between hundreds of origins against hundreds of destinations.
Most distance APIs limit you to 25x25 locations, but Geocodio’s Distance Jobs API can process up to 50,000 distance calculations (e.g., 500 origins x 100 destinations)—80x more than Google and Mapbox’s distance APIs.
The Distance Jobs endpoint sends webhook notifications when complete. So you can just sit back, let Geocodio run the distance calculations in the background, and download the complete results when finished.
This eliminates the need to manage thousands of API requests, handle rate limits, orchestrate retries, and stitch results back together.
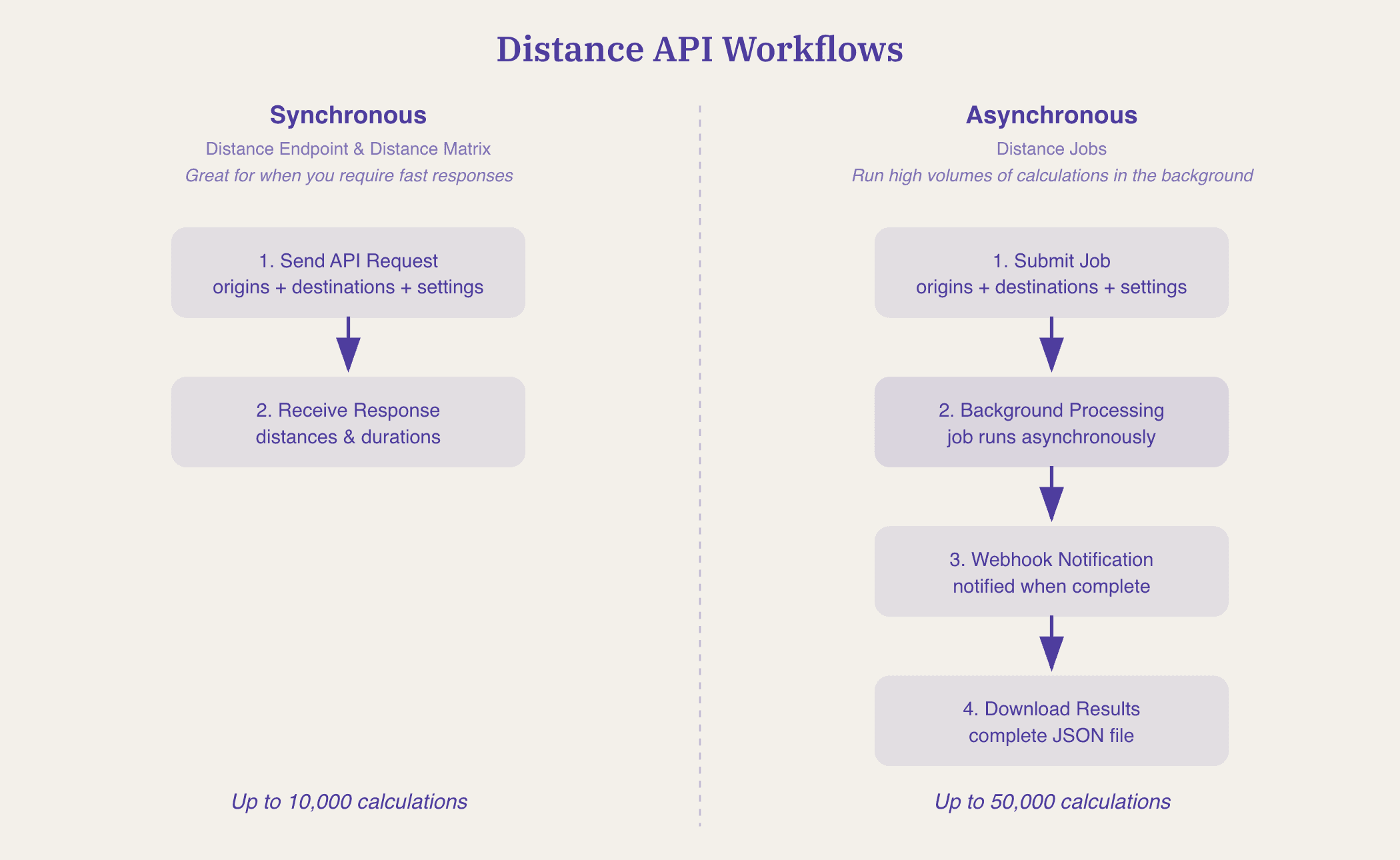
Real-World Use Cases
Marketing: Understanding Customer Geography with Simple Distance Calculation
Let’s say you’re a marketing agency working with fitness clubs to expand their membership. You could use Geocodio’s Distance Jobs API, set on straightline mode, to calculate the distance from a club's address to each member address. As a result, you find that 95% of members live within 7 miles, allowing you to give your direct mail vendor a list of ZIP codes to target for your direct mail campaign radius targets.
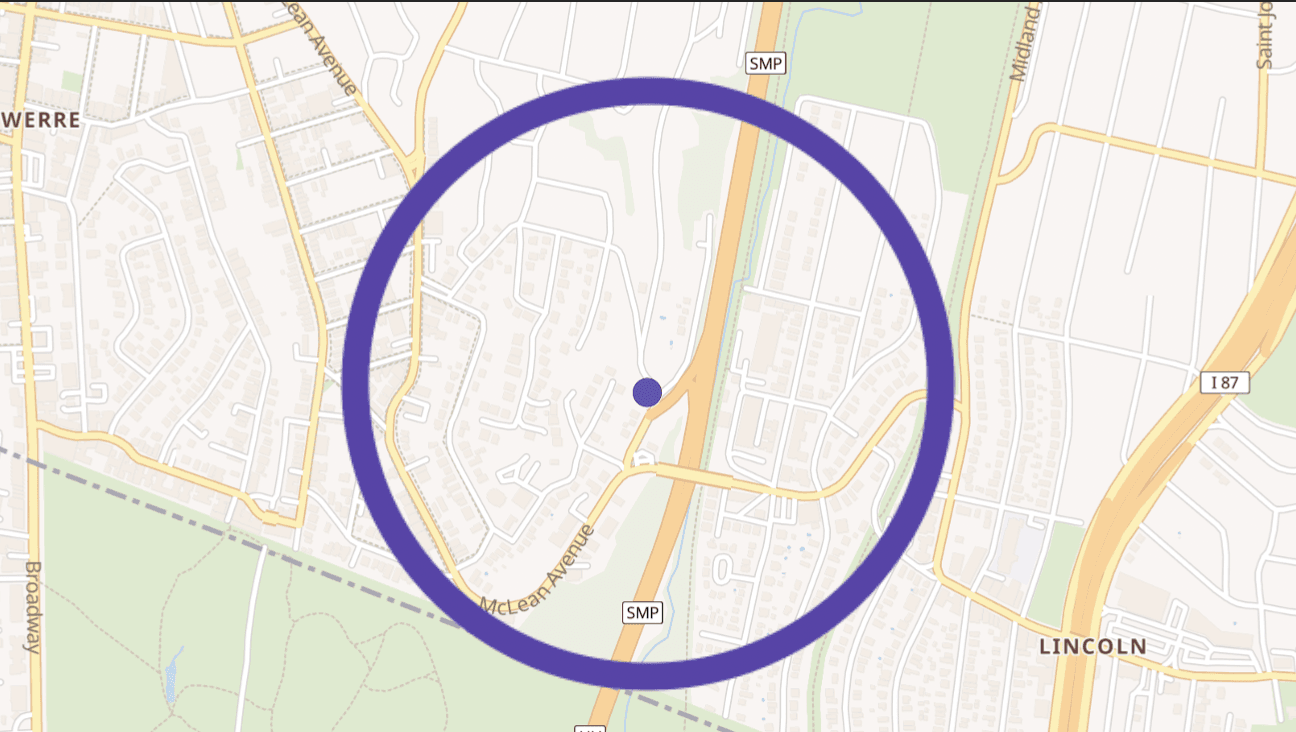
Geocodio’s Distance Jobs endpoint makes this easy, taking the club's address as the origin, and each member address as a destination. The API returns the driving distance for each one (in miles and kilometers), and on your end, you can then bucket them into ranges: 0 to 1 mile, 1 to 2 miles, and so on.
To request a similar distance calculation, first enable Distance for your API key. You can do that on your dashboard.
Here's what the API call looks like calculating distance from a business (a gym) to several clients (member addresses).
GET https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance
?api_key=YOUR_API_KEY
&origin=123 Main St, Denver, CO
&destinations[]=456 Oak Ave, Denver, CO
&destinations[]=789 Pine St, Aurora, CO
&destinations[]=321 Elm Rd, Lakewood, CO
If you’re inputting coordinates, you can add custom IDs to your locations so you can identify them later—just append them after the longitude, like "lat,lng,member-123". This makes it easy to match results back to your database. For addresses, you can do a string match.
For this use case, straightline mode provides sufficient accuracy since the goal is understanding geographic distribution rather than actual driving routes.
&mode=straightline
Healthcare: Patient Provider Finders That Filter by Driving Distance
Healthcare websites use filtering to show patients nearby medical centers or clinics. A single call to Geocodio’s Distance API can return all clinics within a 15-mile driving radius, limited to the 5 closest results and sorted by distance:
GET https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance
?origin=patient_address
&destinations[]=clinic_1&destinations[]=clinic_2...
&max_distance=15
&max_results=5
&order_by=distance
&sort_order=asc
You can also filter by drive time. Use max_duration with a value in seconds (1800 for 30 minutes). Use min_distance and min_duration if you need to exclude locations that are too close.
These filters apply to all the distance endpoints, including the async jobs we'll cover shortly.
Service Companies: Estimated Arrival Times
Appliance and appliance service companies can use Geocodio’s Distance API to provide customers with ETAs. When a technician clicks "On My Way" at 9:22 AM, a simple API call calculates the driving time from their current location to the customer's address.
Companies don't need turn-by-turn directions—their technicians use Google Maps or Waze for that. What they need is approximate driving time, reliably, at scale.
Note: Geocodio’s Distance API uses average travel times, and it doesn’t take real-time traffic into account.
This is a simple Distance API call. Origin is the technician's current location, and destination is the customer's address.
Example request:
GET https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance
?origin=technician_current_location
&destinations[]=customer_address
&mode=driving
The response gives duration_seconds, which is added to the current time to get the ETA.
Example response:
{
"duration_seconds": 3060,
"distance_miles": 28.4
}
For example, 3,060 seconds (51 minutes) added to 9:22 AM gives 10:13 AM. Adding a 10-minute buffer accounts for the fact that these are average travel times, resulting in an ETA window of 10:13 to 10:23 AM.
Healthcare Compliance: Patient Access Reporting with Async Distance Jobs
Some healthcare plan providers are required to report on patient access to care by measuring driving time from patients to facilities. This typically involves massive calculations.
For example, let’s say you have 1,000 patients x 50 clinic locations, which equals 50,000 distance calculations, and you need to filter for only facilities available within a 30-minute drive.
Distance Jobs handles this with a single request.
With Geocodio’s Distance APIs, you can submit sources and directions directly to the Distance Jobs endpoint as an array. You can also upload the lists to Geocodio first.
POST https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance-jobs
{
"name": "2024 Patient Access Report",
"origins": 12345,
"destinations": 67890,
"distance_mode": "driving",
"max_duration": 1800,
"max_results": 1,
"order_by": "duration",
"callback_url": "https://yoursite.com/webhook"
}
The origins and destinations values reference list IDs from spreadsheets uploaded to Geocodio.
Filtering: The max_duration of 1,800 seconds filters to 30 minutes, while max_results of 1 returns only the single closest clinic per patient.
The callback_url parameter means Geocodio will notify your server when processing completes—no polling required.
Retail: Site Selection Analysis with Async Distance Jobs
E-commerce companies opening physical stores need to analyze customer access by measuring travel distance from large customer bases to potential retail locations. They need to find which locations would serve the most customers with the shortest total travel distance.
Geocodio’s Distance Jobs performs these large-scale calculations with just one request.
POST https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance-jobs
{
"name": "Raleigh Store Site Analysis",
"origins": 2500,
"destinations": 20,
"distance_mode": "driving",
"units": "miles"
}
In this example, origins represent potential retail locations (list of retail spaces to lease) while destinations are customer addresses. The results show the distance from each potential site to every customer, enabling analysis of which location minimizes total travel distance.
Check job status with a GET request.
GET https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance-jobs/abc123xyz
{
"status": "PROCESSING",
"total_calculations": 50000,
"calculations_completed": 50000,
"progress": 47
}
Once status shows COMPLETED, download your results.
GET https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/distance-jobs/abc123xyz/download
You’ll get a complete JSON file with every origin-destination pair, distances, and durations.
Combining Distance Calculations with Geocoding
You can calculate distances directly from geocoding requests to Geocodio by simply adding the destinations parameter to any geocode call. Just be sure you’ve enabled Distance API permissions for your API key.
GET https://api.geocod.io/v1.10/geocode
?q=123 Patient St, Chicago, IL
&destinations[]=Clinic A Address
&destinations[]=Clinic B Address
&max_results=3
Get both the geocoded coordinates and the distances to each destination in one response, eliminating the need for a separate API call.
Distance Matrix APIs Compared: Geocodio vs Google Maps, HERE, and Mapbox
How do Geocodio’s Distance APIs compare to other top distance and distance matrix API products?
What Makes Geocodio’s Distance APIs Different
1. Massive Scale Without Orchestration
Most distance APIs cap requests at 25×25 locations, forcing developers to:
- Split data into hundreds or thousands of requests
- Manage rate limits and retries
- Stitch results back together
Geocodio’s Distance Jobs endpoint processes up to 50,000 calculations in a single asynchronous job, returning a complete result set via webhook. This is substantially more than Google Maps and Mapbox distance APIs.
2. Addresses In, Distances Out (No Pre-Geocoding)
Geocodio uniquely allows:
- Raw street addresses as origins and destinations
- Optional coordinates if you already have them
Google, HERE, and Mapbox require coordinates, meaning an extra geocoding step, extra API calls, and more complexity.
3. Built-In Filtering and Sorting
Geocodio’s Distance APIs let you:
- Filter by max/min driving distance
- Filter by max/min driving time
- Sort by distance or duration
- Limit results (e.g., “closest 5 locations”)
Competitors typically return raw matrices that require custom post-processing to achieve the same outcome.
4. Designed for Analytics, Not Navigation
Geocodio’s Distance APIs focus on distance intelligence, not turn-by-turn directions:
- Typical (average) driving times
- Predictable, stable results for reporting and analysis
- Ideal for healthcare compliance, retail and other site selection, market analysis, and ETAs
Google, HERE, and Mapbox are optimized for real-time navigation, which adds cost and complexity when you don’t need it.
Crucially, Geocodio allows you to store the results, which is prohibited by Google and HERE. Mapbox requires a commercial license in order to use their results in production.
5. Simple Endpoint Selection: Sync When Small, Async When Big
Geocodio offers three clear options:
- Distance – real-time, single-origin use cases
- Distance Matrix – synchronous batch (up to 10,000 calculations)
- Distance Jobs – async, up to 50,000 calculations
Competitors require developers to build this workflow themselves.
Detailed Comparison of Geocodio, Google Maps, HERE, and Mapbox Distance APIs
Use the following table to compare several popular distance matrix APIs.
| Feature / Capability | Geocodio | Google Maps (Routes/Distance Matrix) | HERE Matrix Routing | Mapbox (Directions & Matrix) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance + Time Calculations | Yes, Distance API: distance calculation & matrix | Yes, Routes API – Compute Routes & Compute Route Matrix, and Distance Matrix API (legacy) | Yes (Matrix Routing API) | Yes (Matrix API & Directions API) |
| CSV Upload via API | Yes | No | No | Yes (must be pre-geocoded) (CSV) |
| Input Type | Addresses or coordinates (no pre-geocoding required) | Coordinates only (addresses must be geocoded first) | Coordinates only | Coordinates only |
| Matrix Size Limits (per request) | Up to 50,000 calculations possible in bulk workflows (batch processing via Distance Jobs) or 10,000 calculations sync | Max 625 elements (25×25 limitation on Distance Matrix API) or 100 elements for some modes (Google for Developers) | Up to 10,000 origins × 10,000 destinations (HERE) | Max 625 elements (25×25), less for driving-traffic (Mapbox) |
| Async High-Volume Processing | Designed for large scale; can handle tens of thousands of calculations | No native async jobs; possible via splits but limited by max elements per call | Async matrix requests with support for large enterprise matrices, but require custom job management | Limited without account support (Mapbox) |
| Traffic Data Support | Estimated traffic based on average, not real-time conditions | Yes (traffic-aware ETA) (Routes API) | Yes (live & historical patterns) (Traffic in routing) | Yes (via driving-traffic profile) (Mapbox) |
| Transport Modes Supported | Driving | Driving, transit, walking, cycling (Google Maps Modes) | Car, truck, taxi, bicycle, pedestrian, ... (HERE Modes) | Driving, walking, cycling (Mapbox modes) |
| Turn-by-turn navigation | No (not intended for navigation) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Filtering by distance | Yes (min/max distance) | Limited (post-processing required) | Not specified | Yes |
| Sorting results | Yes (by distance or duration, asc/desc) | No native sorting | No native sorting | No native sorting |
| Result limiting | Yes (max_results) | Not specified | Not specified | Not specified |
| Webhook on completion | Yes (async Distance Jobs) | No | No | No |
| Batch orchestration required | No (single async job) | Yes (client must manage batching, retries, stitching) | Yes | Yes |
| Ease of Use / Integration | Simple API with CSV workflows; ideal for bulk distance analysis; significant time and ease-of-use gains from being able to store the results | Rich ecosystem, broad SDK support, but has strict matrix size limits and added complexity associated with real-time navigation features; prohibition on storing results limits use cases | Enterprise-grade SDK & features, but more complex to start (associated with real-time navigation features) and requires coordinate-based input; prohibition on storing results limits use cases | Developer-friendly but constrained by small matrix limits and scaling limitations; also, added complexity associated with real-time navigation features; complex licensing introduces production deployment friction |
| Geographic Coverage | US & Canada geocoding; distances within those regions | Global coverage | Global coverage | Global coverage |
| Data Storage | Permissive terms let you store and re-use the data however you want, without restrictions | Restrictive terms limit storage and use; not permitted to keep results permanently | Restrictive terms limit storage and use; not permitted to keep results permanently | Separate commercial license must be purchased for use of data in production as per terms |
| Pricing | Credit system: straightline distance calculation = 1 credit, driving distance = 2 credits Pay as you go: 2,500 credits/day free, then $1/1,000 credits *Geocoding portion included for Standard and Enterprise Unlimited customers; credits only consumed for distance requests | 10,000 free monthly events; then starting at $5.00/1,000 | 2,500 monthly transactions free; then starting at $4.40/1,000 | Up to 100,000 Directions requests or Matrix elements free / month; starts at $2/1,000 thereafter |
| Pricing Events | Based on number of inputs | Based on number of inputs | Based on number of inputs calculated | Based on elements returned (Matrix API elements) |
Bottom Line: Which Distance API Should You Use?
If you need turn-by-turn navigation or live traffic data, global coverage, and don’t need to store the data, Google or HERE might make sense. If you need to store the data and have the time to negotiate a custom commercial license with them in order to do so, look at Mapbox.
If you’re only interested in locations within the US and Canada and need to calculate driving distance and time at scale and you want to keep the data, with filtering, sorting, and async processing, Geocodio is purpose-built for the job.
How to get started with Geocodio’s Distance API
Geocodio’s new Distance API eliminates the headache of high-volume distance calculations.
- Use the Distance endpoint for synchronous single calculations
- Use the Distance Matrix for synchronous batch processing
- Use async Distance Jobs when you need to go really big and do up to 50,000 calculations
To enable Distance API access:
- Log in to your Geocodio dashboard (Self-Service dashboard, Enterprise dashboard—requires log-in or account creation first)
- Go to API Keys
- Create or edit an API key and enable Distance and Distance Jobs permissions for your API key
For detailed documentation and code examples, visit the Distance API documentation (Self-Service API docs, Enterprise API documentation).
Questions? Feel free to reach out: support@geocod.io.